Learning Management Systems (LMS) have emerged as a key HR Technology component in a modern CHRO’s stack. New technology capabilities such as chatbots, virtual assistants, AI-based training management, and employee experience automation make learning management systems more effective. CHROs no longer rely on traditional classroom-simulated training programs to train their employees, instead, these are done by the new-age eLearning platforms offering instruction-led training and virtual learning.
In this HRTech Primer Series, we will define what is a Learning Management System or LMS, how it fits into a modern CHROs HRTech stack, and the key features you should look out for in an LMS.
What is a Learning Management System?
Learning Management Systems have come a long way in the internet era. Today, LMS has become the crux of HR technology, delivering high-quality content for learning, training, and development, which directly influences employee experience, their engagement rates, and overall retention levels in the organization. It has been found that companies that invest on their learning management systems have much higher success with their employee retention strategies.
Most LMS’ have at least two components. These are:
- Trainer’s interface/ admin interface
- User interface/ learner dashboard
Advanced LMS platforms may also offer a third dashboard called an “evaluator’s interface,” if the learning and performance reporting is outsourced to a third-party team.
Today, HR teams in organizations rely on virtual learning platforms to impart training to employees. Due to the COVID-19 pandemic, organizations have realized the need to adapt quickly to the growing demands of employee training and development.
A learning management system is part of the HR Technology stack by virtue of its association with the Knowledge Management System. An LMS can be easily assimilated into the enterprise tech stack, extending the scope of modern SaaS and Cloud platforms such as Enterprise Content Management Systems, and Sales Enablement platforms. Each LMS vendor has its own version of learning management systems and they define the platform accordingly.
In simple terms, an LMS can be defined as software, a web technology, or a mobile application that is used to create a learning interface between instructors and learners. The LMS may perform one or many functions other than just simplifying learning programs. For example, the Accenture Academy. Accenture LMS is branded as Accenture Academy which provides relevant job-focused content aligned to an employee’s current competency and job. Looking at Accenture’s LMS model, we could evaluate that a powerful LMS is a workforce transformation platform that accelerates learning through new digital concepts such as micro e-learning, content recommendation, competency-based training, and immersive learning.
Recommended HR Tech News: New Data Report from VergeSense Finds Office Utilization Still Fluctuating, and Demand for Collaborative Space is Climbing
What’s a Learning Path that LMS Provides?
We referred to Oracle Learning Management System’s ‘Learning Cycle’. Here’s the graphical representation of OLM’s learning model, which is more or less same for every LMS user.
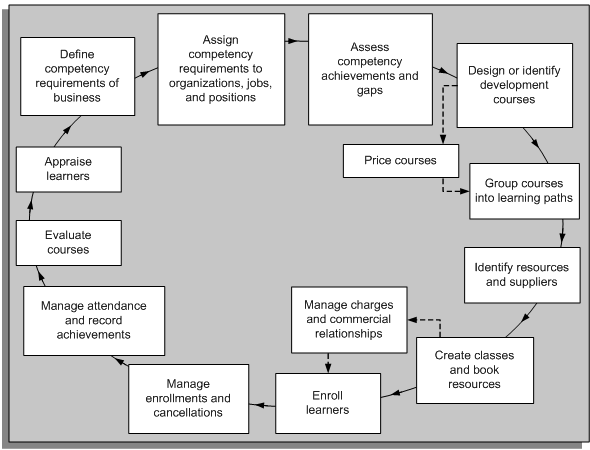
In our quest to refine the definition of Learning Management Systems, we came across Gartner’s Corporate Learning resource page. Gartner’s corporate learning definition aligns with our understanding of enterprise LMS HR Technologies. Gartner says, “Corporate learning solutions include applications that help organizations train, develop and engage their learners. These applications continue to expand the functionality and robustness of their components. Furthermore, they help organizations with compliance, certifications, onboarding, talent development, upskilling, collaboration, coaching and mentoring, sales training, partner education, and customer training.”
Types of LMS
LMS families can be categorized based on different approaches, designs, and functionalities.
For instance, by virtue of their customer base, an LMS could be either:
- Enterprise LMS
- Small business LMS
Based on their usage, it could be:
- Corporate LMS (for business only)
- Academic LMS (for schools and colleges)
From the point of view of an HR Technology integration, LMS could be:
- Self-hosted or proprietary LMS
- Cloud-based LMS
- Open-source LMS
- Mobile app LMS (includes the extended admin roles, user profiles, payments, gaming, and messaging features)
- Self-learner’s LMS (such as LinkedIn, Glassdoor, Udemy, etc)
From an AI perspective, it could be:
- Analytical LMS
- Non-analytical LMS
To meet HR goals, an LMS platform should be able to deliver content in a user-friendly and responsive manner irrespective of the family of LMS it belongs.
Why Should CHROs Invest in an LMS?
A Learning Management System has a direct relation to an organization’s digital transformation journey. Investing in an LMS empowers the HR organization to drive sustainable results with their employee-focused content standards and employee performance tracking activities at a pre and post-training stage.
The reason to invest in an LMS can be understood from the different features an LMS provides at an enterprise level. Some of the key features of an enterprise Learning Management System are:
1) Multi-format content design and sharing – Word, Excel, PowerPoint, PDF, Video, AR /VR
2) AI-based localization and translation with an automated recommendation
3) Real-time instructions and training with chat and virtual assistance
4) Per-user customization and course designing
5) Analytics based employee listening and activity tracking
6) Course completion alerts, notifications, and certifications, and much more.
Extended LMS supports mobile accessibility, skill gap analysis, and gamification of training content and enablement, particularly for high-growth teams such as Marketing, Sales, and Customer Support. Overall, the results and data analysis can be integrated at some level with existing HRIS, Employee analytics, and HCM platforms for a powerful and interactive learning experience at all stages of engagement between HR Teams and the employee (s).
Vendors such as ShareKnowledge (now part of EPAM) also provide a full-fledged LMS testing with social learning LMS suite for HR teams. These platforms are very useful in creating an analytics-driven culture as far as LMS integration and LMS reporting are concerned. With added features linked with AI, no code analytics, voice conversation, back-office automation and RPA techniques, the future of LMS may look very different than what is today. Nonetheless, with so many diverse features and benefits, CHROs are bound to reap ROI from their LMS investments.
Here are the leading LMS platforms for enterprises and SMEs.
Accenture Academy
Accenture Academy currently supports the global demands of an adaptive workforce by using digital technology to reinvent the employee experience and re-designs organizations to be more agile. It has a very powerful LMS curriculum that is publicly accessible.
SAP Litmos
SAP Litmos is a popular LMS in the HR Technology space. It is one of the few LMS platforms that provides remote and offline LMS features to users in 35+ languages.
With zero barriers to learning, SAP Litmos users are able to create, share and access SCORM Content without requiring third-party app support. 30 million users across 150 countries use SAP Litmos to track their performance and course completion records.
Oracle Learning Managemen (OLM)
OLM provides enterprise LMS with cataloged learning paths that help to monitor performance and develop your employees into a knowledgable workforce. OLM meets all the modern content guidelines such as SCORM and IMS QTI. Developed to meet any budget, LMS by Oracle is one of the few platforms that provides “a configurable framework for secure capture, storage, inquiry, and printing of electronic records and electronic signatures (ERES).”
iSpring Learn
For small teams or mid-sized teams running on short deadlines and tight budgets, iSpring Learn is a good option. Its ‘autopilot’ feature is very useful to automatically manage training deadlines, as well as sending invites and reminders. Greater user security, branched content workflows and interactive courses are some of its other eye-catching features. With its ree mobile app and gamification feature, an HR team can launch its online e-learning initiatives in one day!
Other LMS alternatives that could be included in the review list include:
- TalentLMS
- Paylocity
- Looop
- Moodle LMS
- Lessonly
- Adobe Captivate Prime
- Skilljar
With the perils of “The Great Resignation” looming large on organizations, investing in a good Learning Management System or LMS could companies accelerate their training initiatives to retain the talented workforce.

